THE POWER OF X-RAY SPECTROSCOPY

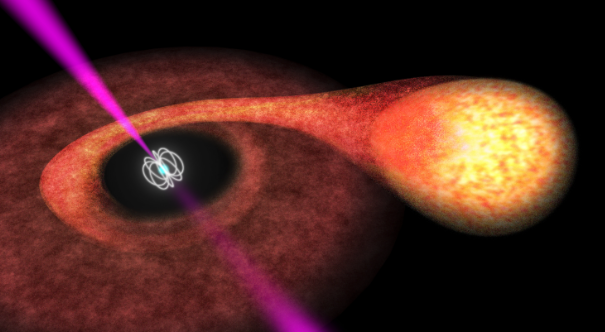
An international conference dedicated to X-ray spectroscopy took place last week in the Polish capital. The conference is funded by AHEAD. Among the various topics presented in the conference were UFOs, acronym for ultrafast outflows: ultra-high velocity jets expelled from supermassive black holes at the core of galaxies.