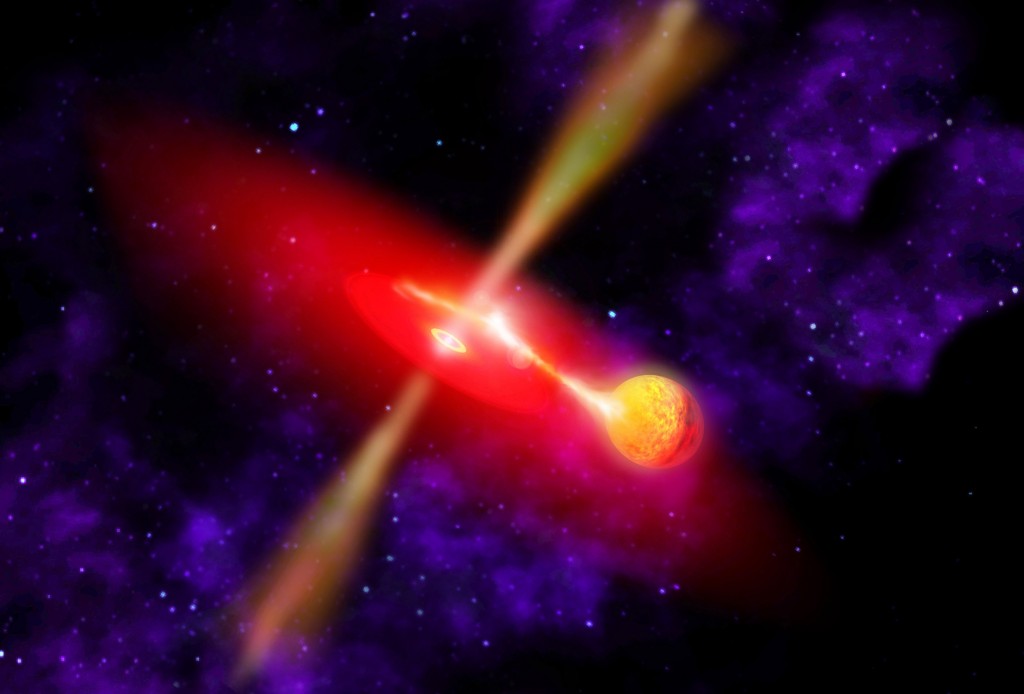
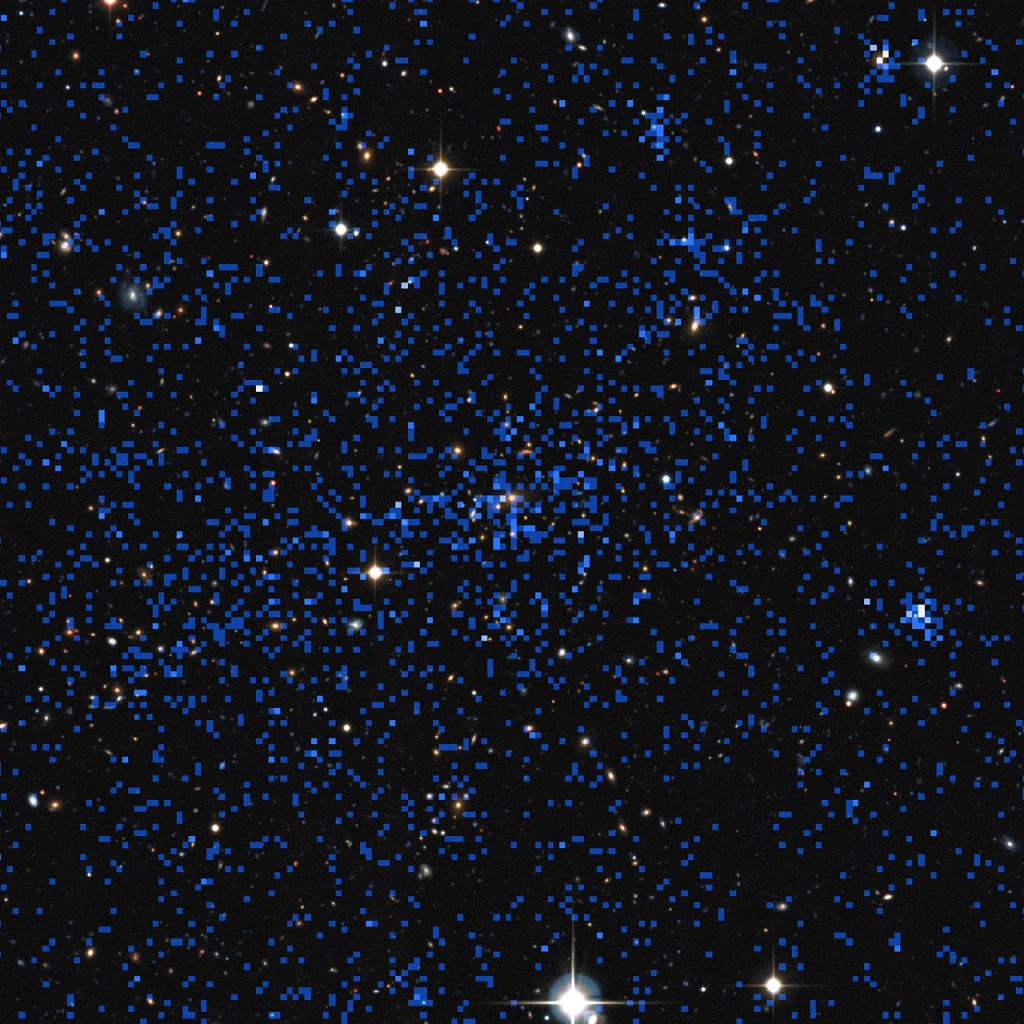
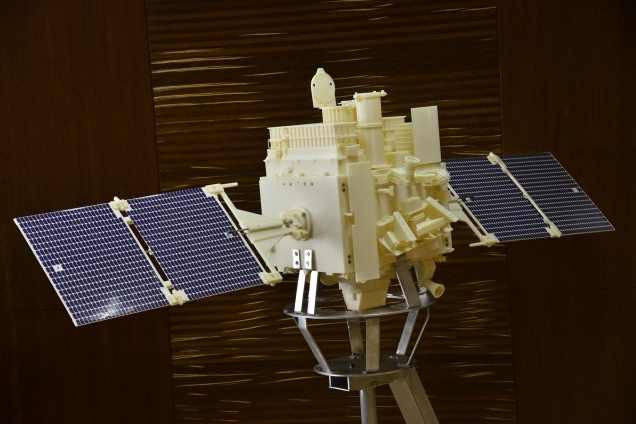
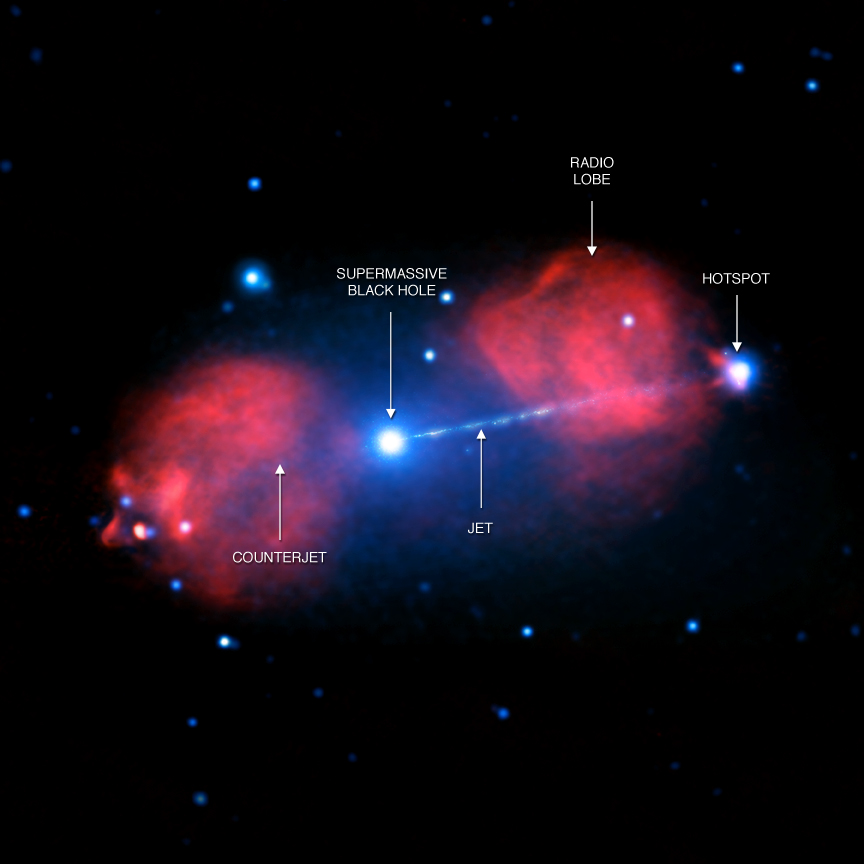
New high energy sources outside our Galaxy were detected with INTEGRAL

A team of astronomers presented a catalogue of 147 high-energy sources, most of them located outside our Galaxy. The detection was made using the INTEGRAL observatory.