The most recent supernova explosion in the Milky Way.
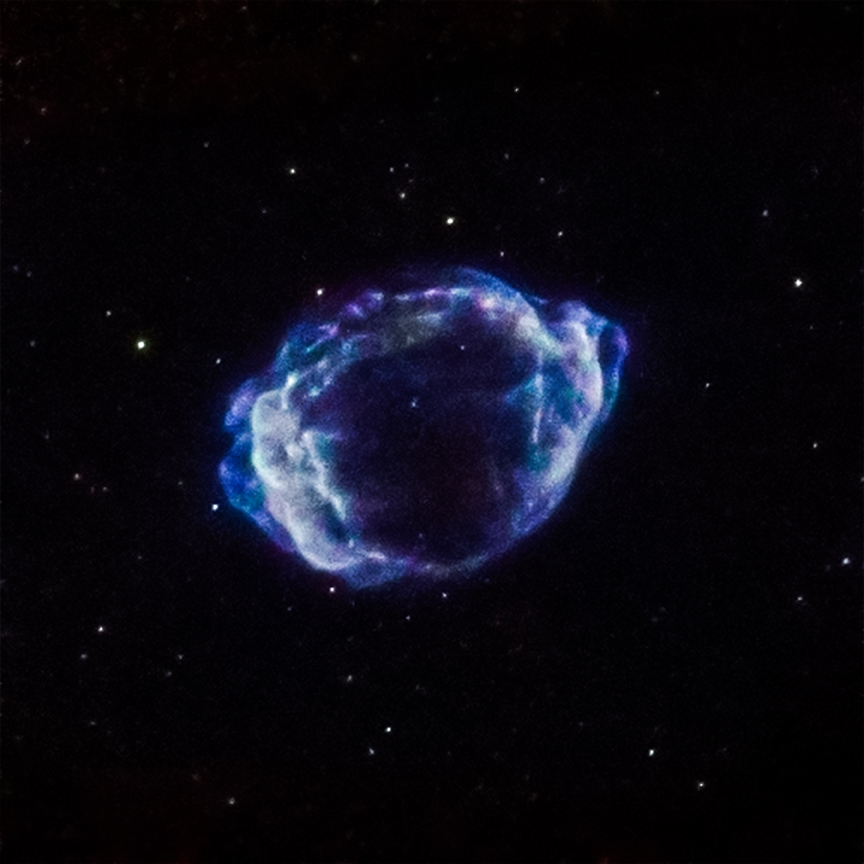

Astronomers used data from the Chandra observatory to find the triggering mechanism of the most recent supernova explosion in the Milky Way.

Astronomers used data from the Chandra observatory to find the triggering mechanism of the most recent supernova explosion in the Milky Way.

On 17th of February, the Japanese satellite Hitomi, the most sensitive X-ray telescope, was launched. On 26th of March, space debris is spotted close to the spacecraft and the communication with the satellite is lost.

Astronomers had the opportunity to capture the very first minutes of a supernova explosion and study the early moments of two dying stars.
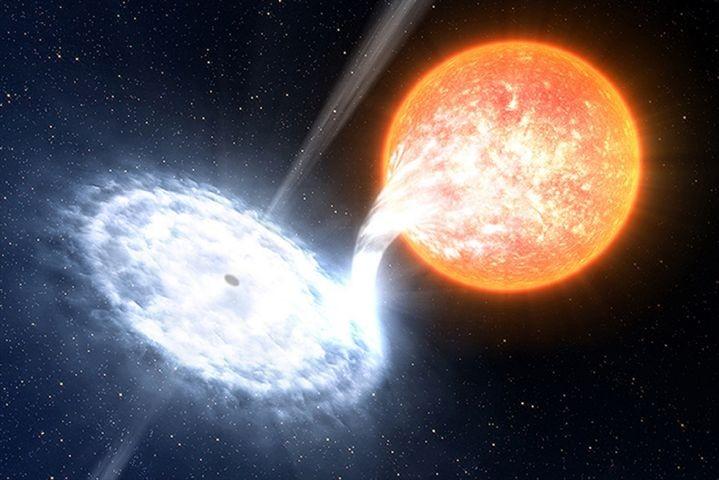

In June 2015, the black hole V404 Cygni showed the most luminous outburst of recent years.
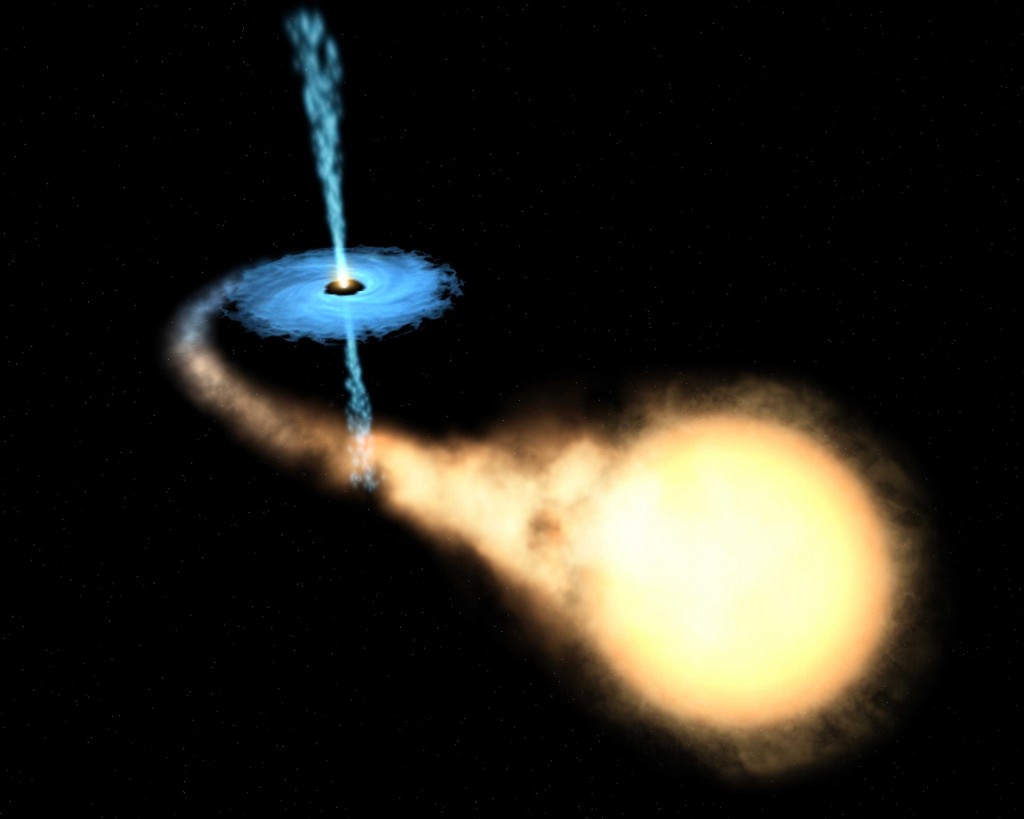
Astronomers used new observations from NuStar and XMM-Newton satellites to reveal the nature of a mysterious X-ray source, located in the Galactic Center region.

The project Einstein@home gives everyone the opportunity to detect a gravitational wave.
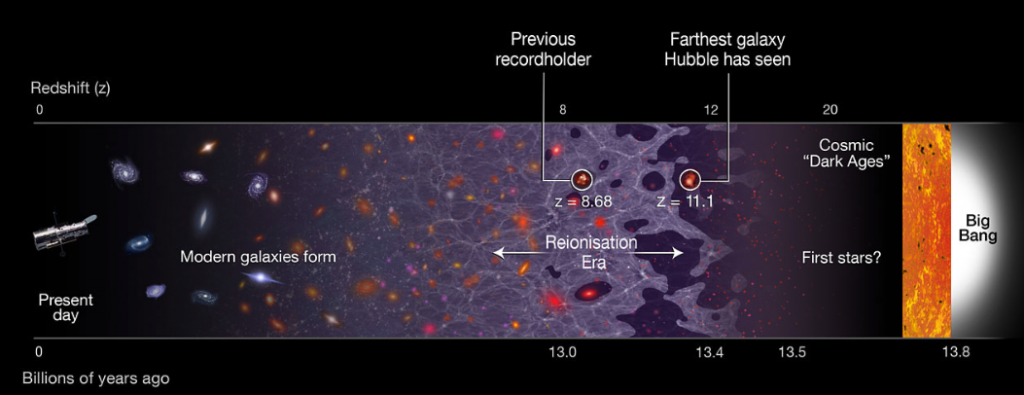
Astronomers used the Hubble Space Telescope to determine the distance of the farthest galaxy that has ever been observed. The galaxy existed only 400 million years after the Big Band, when the Dark Ages of the Universe were just ending and before the cosmic reionization era start. This means that it belongs to the very first galaxies that formed.
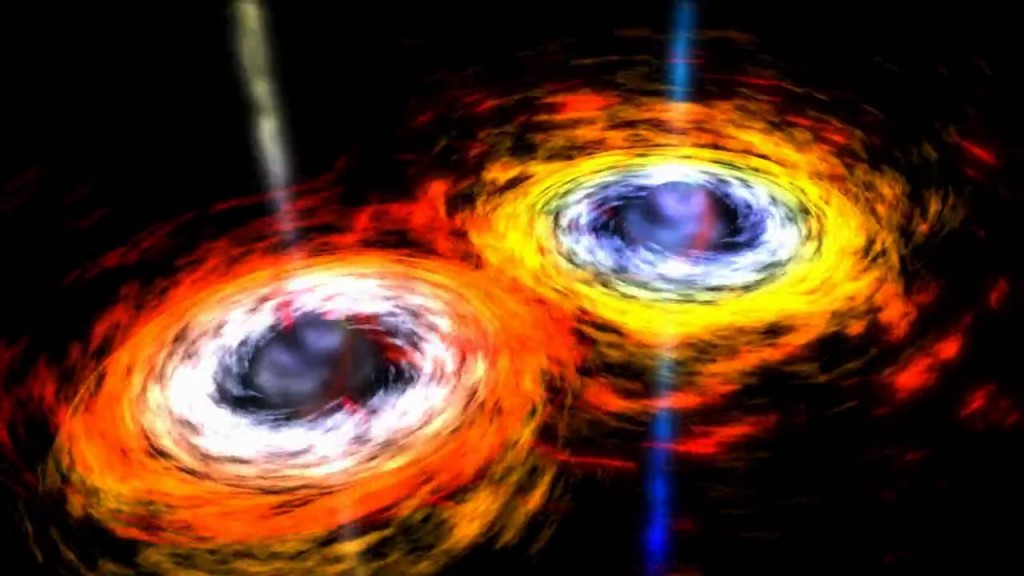

A recent paper by astrophysicist Avi Loeb, of the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics, claims that two black holes can form out of the same dying star.
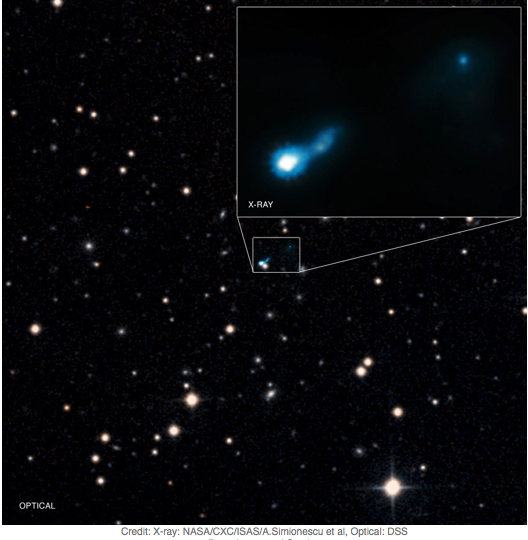

Astronomers discovered an X-ray jet that was emitted from a quasar when the universe was only 2.7 billion years old, using the Chandra X-ray Observatory. The length of the jet is at least 300,000 light years.

On February 17th the X-ray satellite ASTRO-H was launched from the Tahegashima Space Centre. ASTRO-H is capable of observing with unprecedented accuracy the physical mechanisms produced by high-energy phenomena, like supernova explosions and black holes.