How are beautiful swirls of radio emission generated?
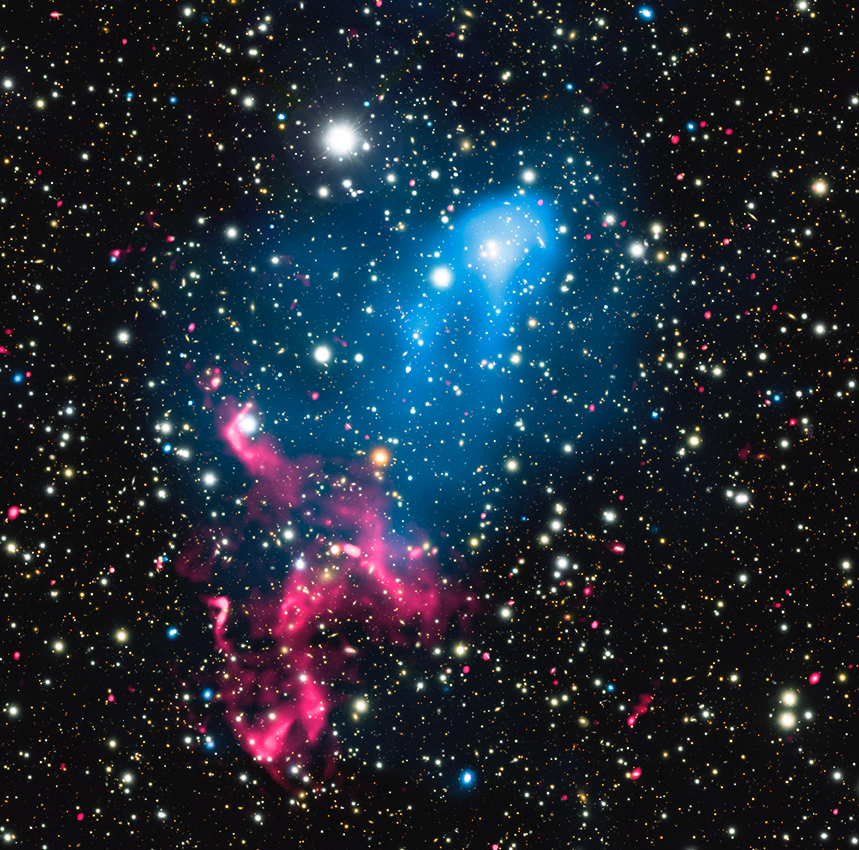

Astrophysicists combined data from the world’s biggest observatories to study what happens to matter that is swept up by the merger of two colliding galaxy clusters.

Astrophysicists combined data from the world’s biggest observatories to study what happens to matter that is swept up by the merger of two colliding galaxy clusters.
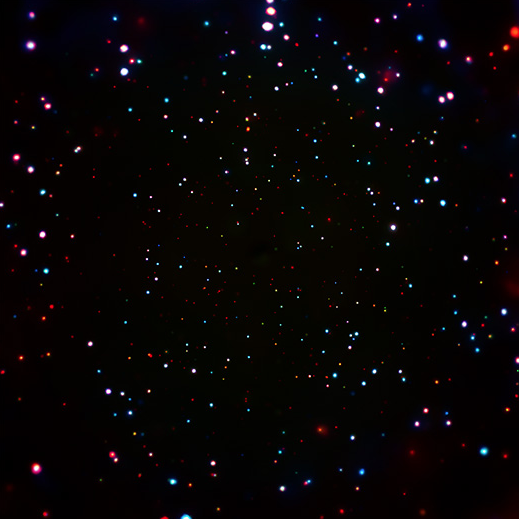

Astronomers used NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory to obtain the deepest X-ray image we have ever observed. It took 7Ms or equivalently eleven and a half weeks of observing time to construct this amazing picture.
A very important process in observational astronomy is to carefully subtract the background noise from an image taken by an X-ray telescope. This background noise may come from background photons, i.e., photons not associated with the source that is being observed or artefacts from the telescope itself. For that purpose, scientists develop software tools that are used to analyse observations taken by X-ray telescopes.

AHEAD’s planetarium movie “The Hot and Energetic Universe”, directed by Theofanis Matsopoulos, won the Golden Star Award at the international fulldome video competition.

In June 2016 astronomers detected what was thought to be the brightest supernova ever observed. Later this year, new observations of the source, complicated things as they revealed phenomena never seen for a supernova. Now, new observations try to shed light on the nature of this source.

Astronomers discovered a galaxy, known as SPT 0346-52, that lies 12.7 billion years from Earth and undergoes an extraordinary rate of star formation.
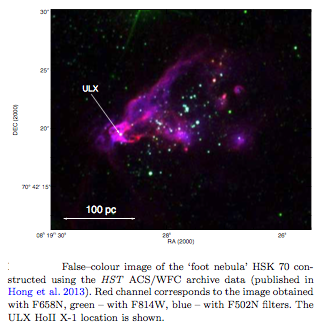
First direct evidence of an Ultraluminous X-ray source moving outwards from its parental star cluster.
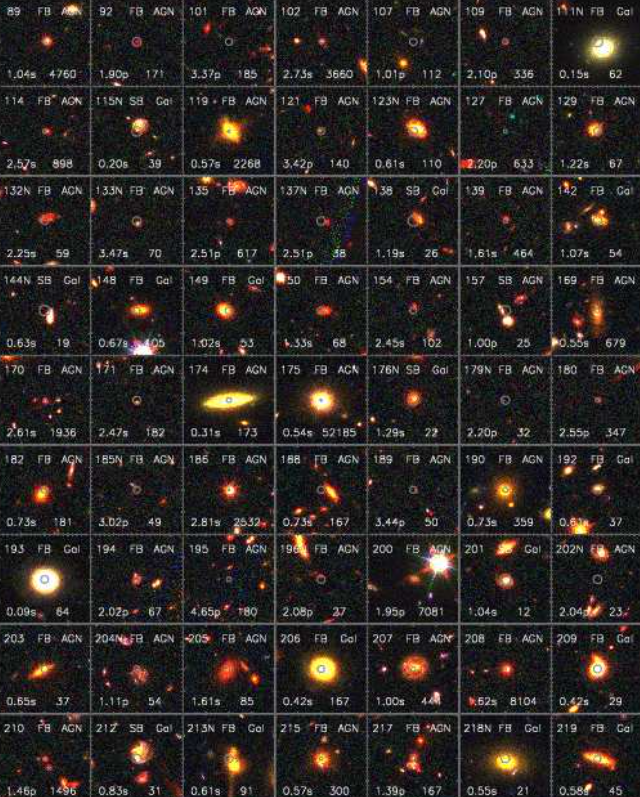
Astronomers took advantage of Chandra satellite’s unprecedented X-ray sensitivity, to create a new X-ray source catalogue. This new catalogue will help scientists investigate how Supermassive Black Holes (SMBHs) grow and co-evolve with galaxies and examine how the X-ray binary populations of starburst and normal galaxies evolve over most of cosmic time, among other exciting things.

AHEAD’s movie “The Hot and Energetic Universe”will be presented on Monday 28th November 2016, simultaneously at the New Digital Planetarium of the Eugenides Foundation, in Athens and the NOΕSIS Planetarium in Thessaloniki, in Greece.

A collision between two galaxies leaves a super massive black hole nearly naked, wandering though space.